What is the Intermediate Value Theorem? Basically, it’s the property of continuous functions that guarantees no gaps in the graph between two given points. In this article, what you need to know about Intermediate Value Theorem for the AP Calculus exams.
- 1.7 Intermediate Value Theoremap Calculus Solver
- Mean Value Theorem
- 1.7 Intermediate Value Theoremap Calculus 2nd Edition
The Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT)
- In this section we learn a theoretically important existence theorem called the Intermediate Value Theorem and we investigate some applications. 1.10 Definition of Derivative In this section we learn the definition of the derivative and we use it to solve the tangent line problem.
- Jul 17, 2017 The Intermediate Value Theorem is useful for a number of reasons. First of all, it helps to develop the mathematical foundations for calculus. In fact, the IVT is a major ingredient in the proofs of the Extreme Value Theorem (EVT) and Mean Value Theorem (MVT). Solving Equations (Bisection Method).
Download Packet: AP Calculus AB / IB Math SL Unit 1: Limits and Continuity Lesson 7: Intermediate Val.
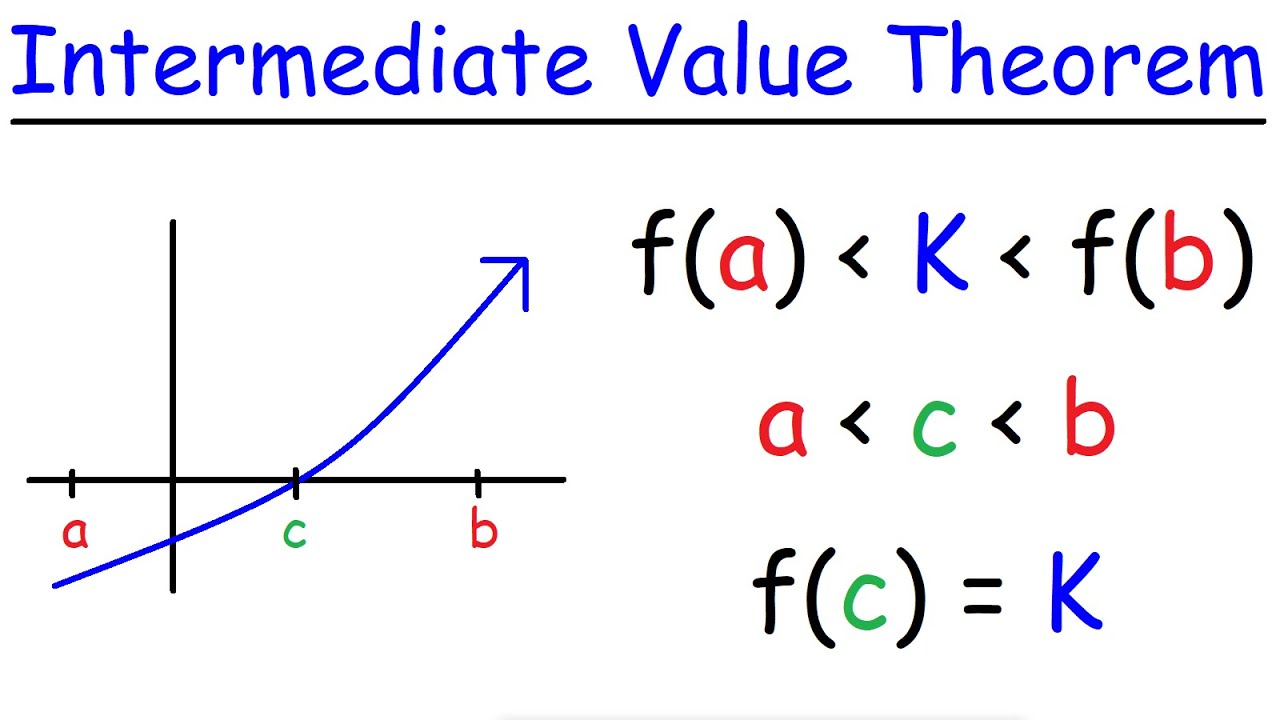
Here’s the statement of the theorem:
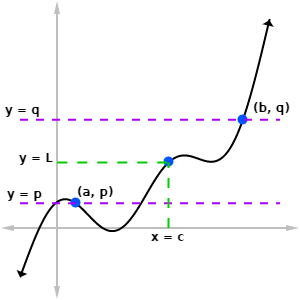
Haunt the housewatermelon gaming. Suppose f is a function that is continuous on the closed interval [a, b]. If L is any number between f(a) and f(b), then there must be a value, x = c, where a < c < b, such that f(c) = L.
Intuitive Understanding of the IVT
So what does this theorem really say? Wrapped up within the mathematical language, there is a simple core idea. If there are two points (a, p) and (b, q) on the graph of a continuous function, and all of the y-coordinates between p and q must also be represented on that function. Here, p = f(a) and q = f(b) as in the theorem.
It may help to think of “L” as a target value. Then the IVT is a statement about whether a function is guaranteed to hit that target value.
If L is any number between the y-coordinates, p and q, then there must be a point x = c so that f(c) = L (as long as the function f is continuous).
It’s as easy as crossing the street…
Suppose you’re standing on one side of a busy street and your friend is standing on the other side, but much further down the street. As you walk toward your friend, you know that you must cross the street at some point in your journey to meet your friend, right?
Think of you and your friend as the two given points in the plane. Your path as you walk down the street is like the graph of a function. The street is simply an “intermediate value” that your path must cross if you want to meet up with your friend. Temperature notification app macsalenew.
Desert road (Photo by William Warby, via Wikimedia Commons)
What Could Go Wrong?
The Intermediate Value Theorem is true so long as the conditions (or, hypotheses) are met. In the case of the IVT, there is one condition: The function must be continuous on the given closed interval, [a, b].
So what happens if a function fails to meet those conditions? Basically, all bets are off.
For example, the function f(x) = 1/x is not continuous on the interval [-1, 1]. Therefore, we cannot expect there to be a value x = c such that f(c) = L for any number L between f(a) and f(b).
In this case, f(a) = f(-1) = -1, and f(b) = f(1) = 1. So, in particular, there’s no guarantee that f(c) = 0 for any value c in [-1, 1]. In fact, the graph of 1/x shows how it completely misses y = 0.
There is no value x = c between -1 and 1 such that f(c) = 0.
What’s It Good For?

The Intermediate Value Theorem is useful for a number of reasons.
1.7 Intermediate Value Theoremap Calculus Solver
First of all, it helps to develop the mathematical foundations for calculus. In fact, the IVT is a major ingredient in the proofs of the Extreme Value Theorem (EVT) and Mean Value Theorem (MVT).
Solving Equations (Bisection Method)
On a more concrete level, the IVT plays a role in solving equations. Suppose you have an equation to solve, such as x3 – 5x = 1.
Based on the graph of the function f(x) = x3 – 5x, we might guess that f(x) = 1 somewhere between x = 2 and x = 3. But how can we be sure? And how can we narrow down our estimate?
Mean Value Theorem
First of all, the Intermediate Value Theorem will guarantee the existence of a solution to the equation, as long as the conditions match those of the theorem.
- Is the function continuous on the interval? Yes, in this case f(x) is a polynomial, which is continuous at all real numbers.
- Is the target value between f(a) and f(b)? Well let’s find out! Here, we let a = 2 and b = 3. Then we have:
- f(a) = (2)3 – 5(2) = -2.
- f(b) = (3)3 – 5(3) = 12.
Notice that the target value L = 1 is between -2 and 12.

Therefore, by the IVT, there must be a value x = c, where 2 < c < 3, and such that f(c) = 1.
Next, we can narrow down the location of the solution by using the Bisection Method. First find the midpoint between the two x-values. In this example, that would be 2.5.
Then, plug in x = 2.5 into the function.
f(2.5) = (2.5)3 – 5(2.5) = 3.1.
Now check to see which half of the interval contains our target value. Because L = 1 is between -2 and 3.21, we can focus on the smaller interval [2, 2.5]. By the IVT, the solution must be in this interval!
In fact, the Bisection Method can be repeated any number of times until we find the solution to the desired accuracy.
- The midpoint between 2 and 2.5 is: 2.25. f(2.25) = 0.14, which is lower than our target value. Thus, the solution must be in [2.25, 2.5].
- The midpoint between 2.25 and 2.5 is: 2.375. f(2.375) = 1.52, which is higher than our target value. Thus, the solution must be in [2.25, 2.375].
After a few more bisections, you can narrow down the solution to the equation, which is c = 2.33, accurate to two decimal digits.
Summary
- The Intermediate Value Theorem (IVT) is a precise mathematical statement (theorem) concerning the properties of continuous functions.
- The IVT states that if a function is continuous on [a, b], and if L is any number between f(a) and f(b), then there must be a value, x = c, where a < c < b, such that f(c) = L.
- The IVT is useful for proving other theorems, such that the EVT and MVT.
- The IVT is also useful for locating solutions to equations by the Bisection Method.
Improve your SAT or ACT score, guaranteed. Start your 1 Week Free Trial of Magoosh SAT Prep or your 1 Week Free Trial of Magoosh ACT Prep today!
More from Magoosh
About Shaun Ault
Shaun earned his Ph. D. in mathematics from The Ohio State University in 2008 (Go Bucks!!). He received his BA in Mathematics with a minor in computer science from Oberlin College in 2002. In addition, Shaun earned a B. Mus. from the Oberlin Conservatory in the same year, with a major in music composition. Shaun still loves music -- almost as much as math! -- and he (thinks he) can play piano, guitar, and bass. Shaun has taught and tutored students in mathematics for about a decade, and hopes his experience can help you to succeed!
1.7 Intermediate Value Theoremap Calculus 2nd Edition
Leave a Reply
Magoosh blog comment policy: To create the best experience for our readers, we will approve and respond to comments that are relevant to the article, general enough to be helpful to other students, concise, and well-written! :) If your comment was not approved, it likely did not adhere to these guidelines. If you are a Premium Magoosh student and would like more personalized service, you can use the Help tab on the Magoosh dashboard. Thanks!
